

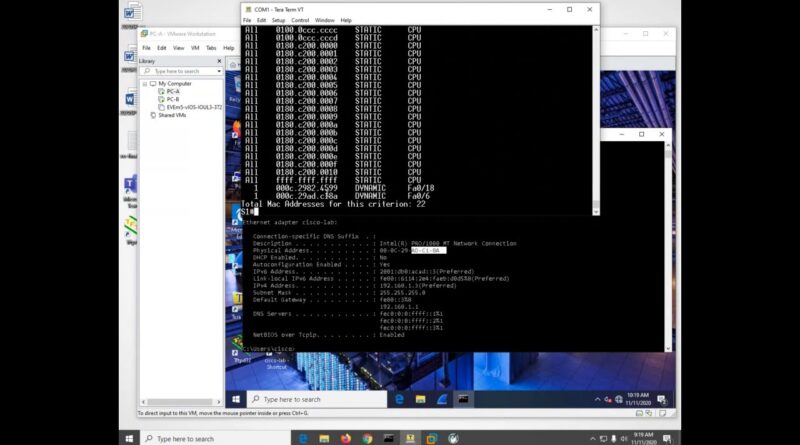
Part 2: Examine the Switch MAC Address TableĪ switch learns MAC addresses and builds the MAC address table, as network devices initiate communication on the network. Assign class as the privileged EXEC password.Assign cisco as the console and vty passwords.Configure IP address as listed in Addressing Table.Configure device name as shown in the topology.Step 4: Configure basic settings for each switch. Step 3: Initialize and reload switches as necessary. Part 1: Build and Configure the Network Step 1: Cable the network according to the topology. If using another model Cisco switch, it may be necessary to use an Ethernet crossover cable. Note: The Fast Ethernet interfaces on Cisco 2960 switches are autosensing and an Ethernet straight-through cable may be used between switches S1 and S2. Required ResourcesĢ Switches (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)Ģ PCs (Windows 7 or 8 with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)Ĭonsole cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
#Cisco mac address static manual#
If you are unsure contact your instructor.Īnswers Note: Refer to the Answers Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices. Note: Make sure that the switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Other switches and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Note: The switches used are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) (lanbasek9 image). In Part 2, you will ping various devices and observe how the two switches build their MAC address tables. In Part 1, you will build a multi-switch topology with a trunk linking the two switches. Switches deliver Ethernet frames to host devices identified by network interface card MAC addresses. Switches are used to interconnect and deliver information to computers on local area networks. The way a switch operates has implications for network administrators whose job it is to ensure secure and consistent network communication. It is important to observe and understand the function of a switch and how it delivers data on the network. If the MAC address is unknown, then the frame is broadcasted out of all switch ports, except the one from which it came. If the destination MAC address is a known address, then the frame is forwarded out of the corresponding switch port associated with that MAC address. Then the destination MAC address is looked up in the MAC address table.

The source MAC address is recorded and mapped to the switch port from which it arrived. When a switch receives a frame from a PC, it examines the frame’s source and destination MAC addresses. This process is called building the MAC address table. The switch records host MAC addresses that are visible on the network, and maps those MAC addresses to its own Ethernet switch ports. The purpose of a Layer 2 LAN switch is to deliver Ethernet frames to host devices on the local network. Part 2: Examine the Switch MAC Address Table Background / Scenario Last Updated on Januby Admin 5.2.1.7 Lab – Viewing the Switch MAC Address Table Answers Lab – Viewing the Switch MAC Address Table ( Answers Version)Īnswers Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
